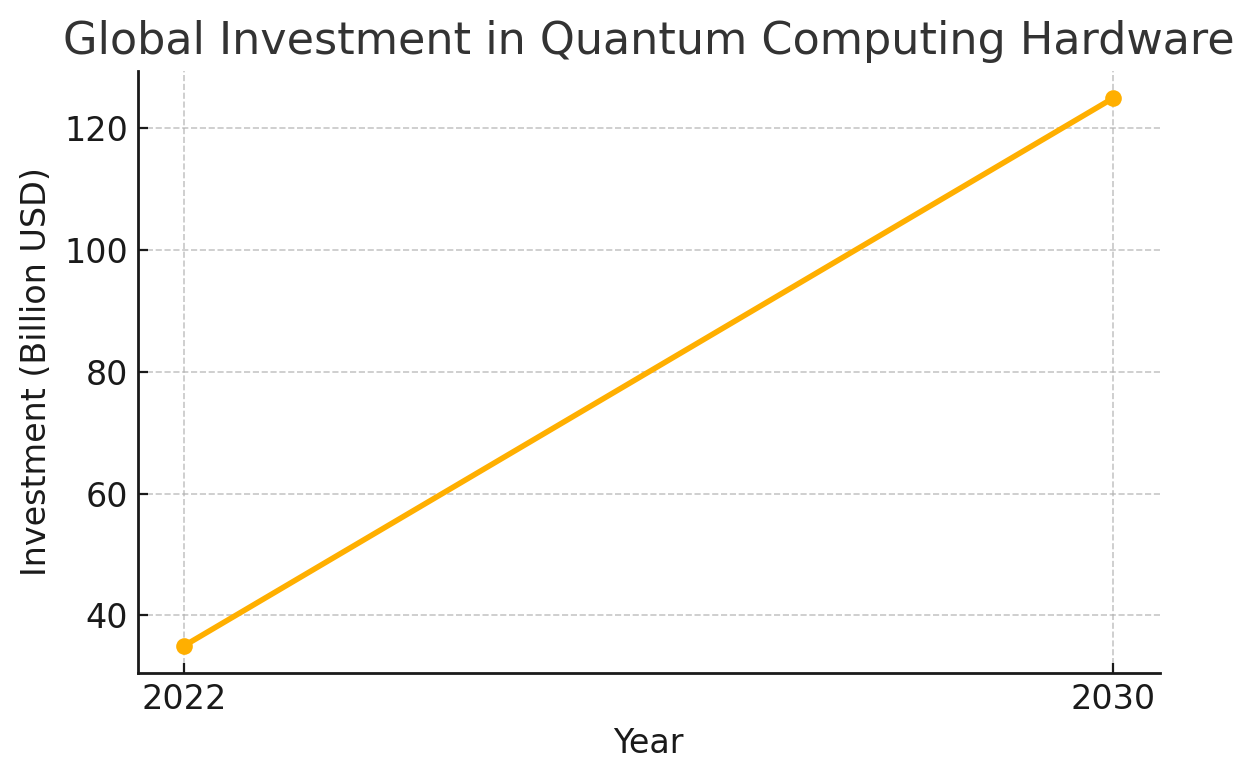
Technology is one of the many challenges that many higher education institutions face today. Providing reliable access to computing resources, storing vast amounts of data securely, and scaling systems to meet demand are essential components of a modern academic environment. Cloud computing offers solutions that can transform how colleges and universities support their missions of teaching, learning, and research.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that provides on-demand access to computing power, storage, databases, and other IT resources. Rather than maintaining expensive physical servers and data centers, institutions can access these resources through the cloud, paying only for what they use. AWS has become a cornerstone of digital transformation in higher education.
AWS can serve as a flexible technology foundation for academic institutions. It can help universities scale resources during peak registration periods, support computationally intensive research projects, and provide students with hands-on experience using industry-standard tools. At URI, AWS infrastructure could support various teaching and learning needs by providing secure, scalable, and cost-effective technology solutions. For example, AWS can:
- Enable virtual labs and development environments where students can practice real-world technical skills
- Host learning management systems and student applications such as Brightspace that need to scale during high-traffic periods for example around final exams.
- Provide computing power for research projects requiring data analysis, machine learning, or simulation
- Offer secure storage solutions for institutional data, research materials, and digital archives
Imagine a faculty member teaching a data science course. Students need access to powerful computing resources to analyze large datasets and build machine learning models, but the university’s physical computer labs have limited capacity. Using AWS, the instructor sets up virtual environments where each student has their own workspace with the necessary tools and computing power. Students can access these resources anytime, from anywhere, completing assignments on their own schedules. This flexible approach highlights an important benefit for teaching and learning: it removes barriers to access, enables hands-on practice with industry tools, and prepares students for careers where cloud computing skills are in high demand.

While AWS cannot replace the expertise of IT professionals and educators, it enhances institutional capabilities by providing enterprise-grade infrastructure without the capital investment of building and maintaining physical data centers. It allows universities to respond quickly to changing needs, experiment with new technologies, and focus resources on their core educational mission rather than infrastructure management.
AWS services, available through institutional partnerships and education programs, support teaching and learning by providing students with hands-on experience using the same tools employed by leading organizations worldwide. Programs like AWS Educate and AWS Academy offer free resources, training, and credits specifically designed for educational institutions. By combining cloud infrastructure with thoughtful pedagogical design, educators can create more dynamic, accessible, and career-relevant learning experiences. At the same time, AWS is just one option among many cloud providers, and institutions can decide whether it aligns with their strategic priorities and technical requirements.
AWS is a partner in innovation. It helps institutions modernize their technology infrastructure, expand access to powerful computing resources, and prepare students for a workforce increasingly built on cloud technologies. By supporting flexibility, scalability, and experimentation, AWS makes advanced technology more accessible and cost-effective for both students and educators.



 AI can serve as a digital rehearsal partner. It can help students and faculty draft outlines, refine language, and anticipate audience questions. At URI, AI tools such as Microsoft Copilot can support public speaking preparation by helping users draft outlines, generate ideas, and explore effective ways to engage an audience. For example, AI can:
AI can serve as a digital rehearsal partner. It can help students and faculty draft outlines, refine language, and anticipate audience questions. At URI, AI tools such as Microsoft Copilot can support public speaking preparation by helping users draft outlines, generate ideas, and explore effective ways to engage an audience. For example, AI can: