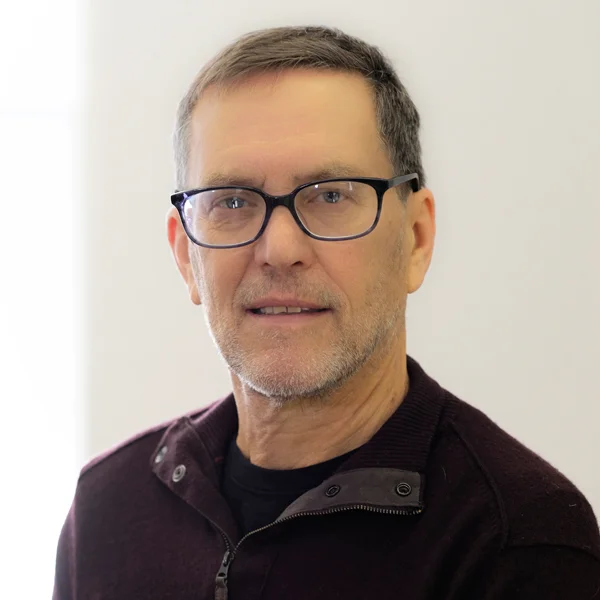
Peter Phipps
Peter Phipps is a part-time faculty member in the Journalism department with 45 years of experience as a reporter, columnist, and senior editor for Providence Journal, Akron Beacon Journal, and Cleveland Press. He has taught Journalism for about 20 years at Emerson and URI.

Introduction
Peter Phipps brings decades of journalism experience to URI’s classrooms, where he teaches a variety of courses including Media Law, History of Journalism, Introduction to Mass Communications, News Writing and Reporting, and Journalism and Criticism. When faced with the challenge of engaging 245 students—140 of them freshmen—in his Introduction to Mass Communications course, Peter recognized that traditional teaching methods wouldn’t suffice. He sought out digital tools that could help him manage such a large class while maintaining student engagement and facilitating meaningful group work.
Throughout his teaching experience, Peter has come to understand a fundamental truth: no matter what tool or professor is involved, student engagement ultimately depends on students’ willingness to participate. This realization led him to develop a multi-faceted approach using three key digital tools: Mentimeter for real-time engagement, Brightspace for course management, and Google Docs for collaborative work.
Mentimeter it’s free for students with lots of polling options, word cloud, multiple-choice questions, etc.
Peter Phipps
Is Mentimeter free?
Yes! Free users can create unlimited presentations with any question type and host up to 50 participants per month. To exceed 50 participants, an account upgrade is required.
Teaching Tool Usage
Before implementing digital tools, Peter had reached out to TLS on several occasions for tools and resources that he could use. He had found their consultation to be helpful in pursuit of which tools URI has as well as support/training for the various functionalities of these tools. This guidance helped him in developing strategies for managing his large class size.
Within the course, Peter structured his 75-minute classes into three carefully planned segments: 35 minutes of lecture, 25 minutes of polling activities and discussion, and 15 minutes for quizzes. To facilitate this structure, he implemented Mentimeter as his primary engagement tool, using it independently of slideshow presentations to conduct real-time polls and create word clouds. While the tool proved effective during periods of high attendance, its inability to track attendance became a significant limitation in a class where he knew only 10 of 245 student names.
The backbone of his course organization relied on Brightspace, where he divided his 245 students into 45 groups. This experience taught him valuable lessons about group dynamics in large classes. Initially creating groups of 5-6 students, he discovered this size was too large for effective collaboration. Through trial and error, he determined that three students per group would be ideal, though this would create the logistical challenge of managing 82 groups.
To facilitate collaborative work, Peter initially used Brightspace’s Locker feature but later transitioned to Google Docs. This platform provided students with more space and flexibility to organize their research and data. Each group designated one member as their document organizer, creating a clear structure for their collaborative work. However, the transition between platforms revealed communication challenges, as some students missed the announcement and continued using Brightspace Locker, resulting in temporary grading complications.
How do my students join a presentation using Mentimeter?
No installation is needed. Students can join by entering the code at menti.com, scanning the QR code, or using the voting link. They can vote directly from their smartphone or internet device.

Sample Word Cloud from Mentimeter
Student Experience & Feedback
The implementation of these digital tools revealed several crucial insights about managing large classes. Student participation demonstrated a clear correlation with physical presence, as attendance dropped dramatically from 240 to 80 to 11 students over time. This decline significantly impacted the effectiveness of interactive tools like Mentimeter. Despite these challenges, some groups showed remarkable engagement with the material. One group particularly stood out by pursuing an academic investigation into the relationship between screen time and eye strain, demonstrating the potential for meaningful research even in a large introductory course.
How to create your first Mentimeter Presentation?
Resources
Mentimeter – A free online polling tool used to create interactive engagement and shape teaching approaches.
Brightspace Groups – Learning management system used for grading and organizing class groups.
Google Docs – Collaborative platform used by groups to collect research data.
View More Faculty Success Stories >>